ExoVasc® PEARS
Menu
- Home
- Medical devices
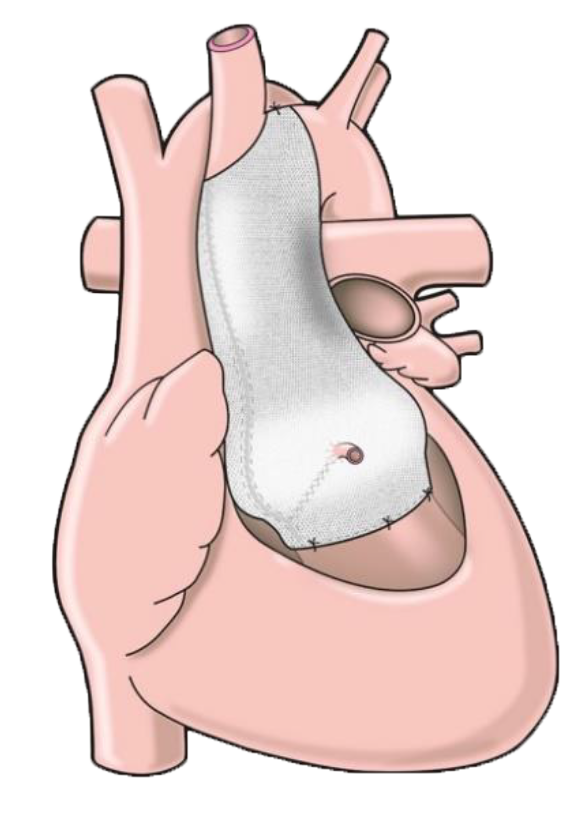
The ExoVasc® PEARS provides an alternative to aortic root replacement. A personalised, custom-made external support is made to exactly match the patient’s aorta.
Learn moreMenuMenu - Useful information
- Patient stories
- News & events
- About



